Article by NOA FO-Aarhus
In the pursuit of understanding and cultivating the skills required for Future Citizenship (FC) in an ever-evolving world, our methodology draws inspiration from and aligns with four prominent European competence models. EntreComp, Lifecomp, DigComp, and GreenComp collectively provide a comprehensive foundation to explore, define, and assess the competencies essential for the Future Citizen.
The first step in constructing our Future Citizen Competence (FCC) model involved defining key terms such as competence, future citizen, (smart) citizen competence, and challenge. A meticulous mapping of FCC’s core competences was undertaken, drawing insights from existing models and scientific evidence. This process ensured a holistic approach, encompassing knowledge, skills, and attitudes vital for navigating the challenges of the future.
A critical aspect of our methodology is the analysis of four key European competence frameworks. EntreComp, designed to foster entrepreneurship skills, LifeComp, focusing on lifelong learning, DigComp, addressing digital competence, and GreenComp, emphasising environmental sustainability, provided invaluable insights. By aligning with these established frameworks, we aimed to capture the multifaceted nature of Future Citizens and ensure our model resonates with contemporary challenges.
Scientific papers were meticulously scrutinised to lay an evidence-based foundation for our framework. The resulting model does not prioritise sub-competencies hierarchically but encapsulates the general construct of FCC. It is a descriptive, learning-outcome-based model, facilitating its integration into educational programs and aligning with the principles of constructive alignment.
Our competency model adopts a holistic perspective, emphasising the interconnectedness of knowledge, skills, and attitudes within a specific context, such as future communities. To ensure relevance and effectiveness, the model underwent validation with specialists and young individuals, aligning outcomes with expectations and real-world challenges.
In essence, our methodology blends the wisdom of established European competence models, empirical evidence, and stakeholder validation to craft a comprehensive Future Citizen Competence model. By acknowledging the dynamic nature of competence and its application in context, we pave the way for a forward-thinking, adaptable, and socially responsible generation of Future Smart Citizens.
How are the Citizen Competences connected?
In this map we illustrate the connections and inner relation between the selected competences. At the basis we find competences associated with mindset, values and beliefs needed in order to navigate the challenges of the future. The next level specifies competences needed to facilitate action, including technological skills and the ability to “read” the future needs and demands. At the top level we find the the competences needed to foster and envision collaboration and community action.
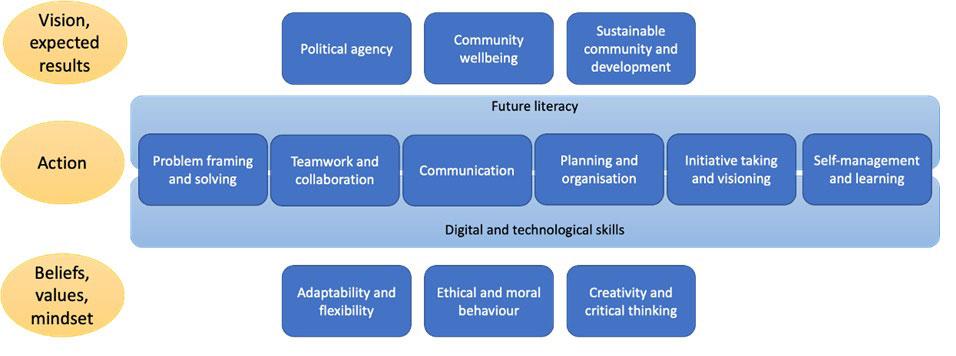
The Citizen Competences: What do you need to know?
1. Political Agency Competence:
- Description: Skills, knowledge, and abilities to actively engage in the political process, contribute to policy making, and drive positive change.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Analyse and synthesise information for informed decisions.
- Evaluate policy proposals for evidence-based policymaking.
- Communicate and collaborate effectively for policy goals.
- Understand cultural diversity and engage in global policy dialogues.
2. Community Wellbeing Competence:
- Description: Knowledge, skills, and attitudes to promote individual and community safety, health, and well-being.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Promote safety, health, and well-being with respect to nature.
- Understand and address community health risks and factors.
- Foster social cohesion and inclusivity.
- Develop evidence-based solutions for community health and well-being.
3. Sustainable Community and Development Competence:
- Description: Skills, knowledge, and abilities for active contributions to environmentally, socially, and economically sustainable communities.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Use digital platforms for advocating sustainable practices.
- Collaborate for responsible and sustainable community development.
- Analyse complex issues and evaluate policy options.
- Generate innovative solutions for sustainable community development.
4. Future Literacy Competence:
- Description: Knowledge and skills for imagining diverse futures and using futures as lenses to perceive the present.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Efficiently access and select information from various sources.
- Apply research methodologies based on needs.
- Analyse, evaluate, and critically interpret data and information.
- Estimate the cost of activities and plan financial decisions.
5. Digital and Technological Competences:
- Description: Knowledge and skills to use technological and digital solutions for information management and interaction.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Analyse information from multiple sources.
- Understand how digital systems and processes work.
- Facilitate learning with technology to support others.
- Manage technology use in digital platforms and virtual environments.
6. Problem Framing and Solving Competence:
- Description: Abilities to solve cross-disciplinary and real-world problems through cognitive skills and critical thinking.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Define and unpack complex problems.
- Generate alternative solutions and select viable options.
- Identify and use appropriate technology for problem-solving.
- Make decisions and take actions based on chosen solutions.
7. Collaboration and Teamwork Competence:
- Description: Knowledge, skills, and attitudes for effective collaboration, shared responsibility, and goal achievement.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Value effective teamwork and understand teamwork principles.
- Motivate and inspire collaboration within a team.
- Fulfil necessary roles for moving towards common goals.
- Lead collaboration processes as needed.
8. Communication Competence:
- Description: Use of communication strategies, codes, and tools to express oneself, understand others, and achieve social goals.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Process social information and be open to communication.
- Use negotiation and presentation skills effectively.
- Interact through digital technologies for information sharing.
- Extract, assess, and generalise important information.
9. Planning and Organization Competence:
- Description: Abilities to determine goals, assess actions, and manage resources for goal achievement.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Set short- and long-term goals and priorities.
- Formulate action plans based on goals and available resources.
- Manage resources for turning ideas into action.
- Analyse processes and environments for feedback and changes.
10. Initiative Taking and Visioning Competence:
- Description: Attitudes and ability to identify opportunities, understand changes, and create innovative solutions.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Identify and analyse social, cultural, and economic changes.
- Mitigate risks and combine knowledge for goal achievement.
- Create innovative solutions based on new knowledge.
- Develop a vision to turn ideas into action.
11. Self-Management and Learning Competence:
- Description: Skills for maintaining motivation, self-belief, and orientation to long-term goals.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Reflect on needs, aspirations, and wants in the short, medium, and long term.
- Use initiatives for value creation and as learning opportunities.
- Reflect and learn from success and failure.
- Turn ideas into action and remain resilient under pressure.
12. Adaptability and Flexibility Competence:
- Description: Knowledge, skills, and attitudes to cope with changes and challenges, integrating new information effectively.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Adapt to and meet changes as they arise.
- Recognize and understand the need for change.
- Understand and negotiate diverse views for solutions.
- Define boundaries regarding resource management and mitigate risks.
13. Ethical and Moral Behaviour Competence:
- Description: Knowledge and actions that define right and wrong behavior, aligning with ethical principles.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Respect and understand ethical and moral norms of society.
- Behave in line with ethical and moral values.
- Use moral judgement skills in decision-making.
- Have a willingness to do good.
14. Creativity and Critical Thinking Competence:
- Description: Use of imagination, original ideas, and critical thinking to analyse facts and make rational judgments.
- Learning Outcomes:
- Compare, analyse, and synthesise data to draw logical conclusions.
- Develop a vision to turn ideas into action.
- Explore and experiment with innovative approaches.
- Be aware of biases, question assumptions, and use evidence for critical thinking.
These competences collectively equip Future Citizens with a comprehensive set of skills and attitudes necessary for thriving in an evolving world and contributing to positive societal development.






